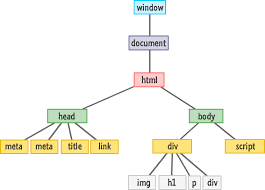
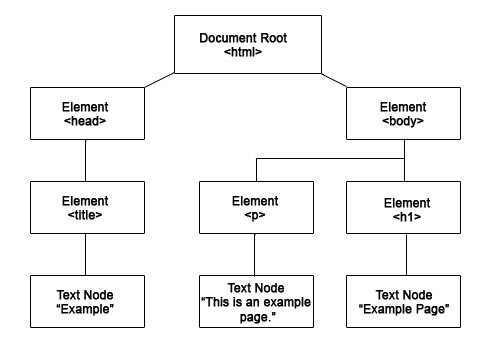
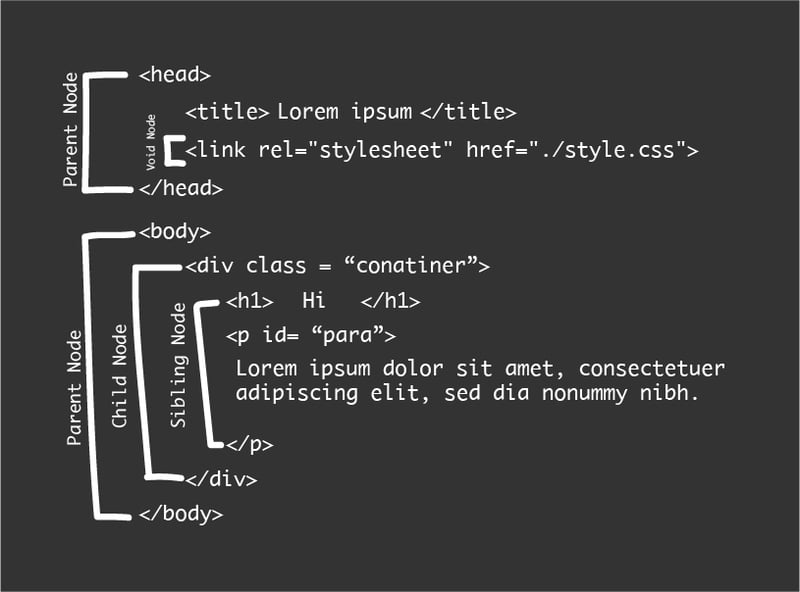
DOM or Document Object Model is a representation of the web page or document, which can be modified with a scripting language such as JavaScript according to MDN.
It characterizes the DOM HTML document as a hierarchical tree structure and each element in the document tree is called a Node.
DOM nodes represent all components that make up a web page. For example, a head tag is considered to be a node. Most nodes have a starting tag and ending tag. Things can be nested inside these tags. The inner node is called a child node and the outer node is considered to be its parent node.
Some nodes are self-closing tags like the "img" tag. These are called void nodes and cannot be a parent node, meaning things can’t be nested within them.
Since 'document' is an object which has properties and attributes, it will have properties & methods. In order to access things within an object, we use selector and query methods to change the content displayed in the browser.
Element Selectors
document.getElementById("idName")
//This method only returns the one element by the specified ID.
document.getElementByClass("className")
//This method returns all elements inside the whole document by the class you specified.
document.getElementById("someElement").getElementsByClassName("className")
//It works in all elements of the DOM, this will return all elements by the class you specify inside the element you want
Query Selectors
document.querySelector("#idName")
//This method takes one argument, which is a CSS selector & returns the first element that matches the selector.
document.querySelectorAll(".className")
//Works similar to above; returns a node list collection of all matching elements.
Create an Element
APPEND
document.createElement("body")
//this method creats the element, but it does not show up on the page.
document.body.append(element)
//this method gets the element to appear on the page.
.INNERHTML
<h1 id="greetings"> HELLO </h1>
let element = document.querySelector("#greeting")
element.innerHTML = "Welcome"
//selects the h1 called greetings and changes HELLO to welcome
Changing Attributes
const element = document.querySelector(".container")
element.style.backgroundColor="#f0f0f0"
//changes the selected elements(in this case the container class) color to grey
Removing Elements
element.remove()
//removes a whole element from the page
This is just a basic overview of some of the methods used to manipulate the DOM.