Data preprocessing might not be the most glamorous topic in the AI, but trust me, it's a crucial step that often gets overlooked. It works behind the scenes and ensures that our language models can effectively comprehend and utilize the information we feed them.
In this blog post, we'll understand the process of data preprocessing, exploring its importance, challenges, and best practices. By the end, you'll have a solid understanding of how to prepare your data for seamless integration with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) applications.
The Importance of Data Preprocessing for RAG Applications
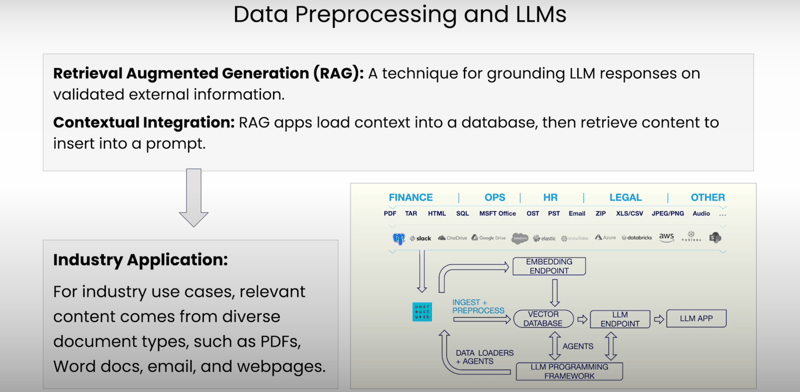
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty details, let's start with a quick primer on retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This fancy term refers to a technique that allows language models to ground their responses on validated external information, such as your company's data or industry-specific data bases.
Instead of relying solely on its internal knowledge, RAG equips it with the ability to consult external sources, ensuring that its responses are well-informed and tailored to your specific needs.
Now, here's where data preprocessing comes into play. Imagine trying to have a conversation with someone who speaks a completely different language – it's going to be a real struggle, right? Similarly, language models need our help to understand the diverse range of data formats out there, from PDFs to PowerPoint slides and everything in between.
Data preprocessing is the process of translating these various document types into a language that our language models can comprehend. It's like having an interpreter by your side, ensuring that the information flows seamlessly between you and your language model.
What is Data Preprocessing?
At its core, data preprocessing involves three main steps:
Extracting Document Content: We need to extract the actual text content from the documents, as this will form the basis for our prompts and queries.
Identifying Document Elements: Documents aren't just walls of text; they're carefully structured with titles, lists, tables, and other building blocks. Data preprocessing helps us identify and categorize these elements, allowing us to leverage them for various tasks like chunking and filtering later on.
Extracting Metadata: Have you ever tried to find a specific document in a messy pile, only to realize you forgot to label them? Metadata is like those labels, providing crucial information about each document, such as page numbers, file types, and more. This metadata becomes invaluable when we need to perform operations like hybrid search or filtering.
By breaking down documents into their core components – text, elements, and metadata – we set the stage for our language models to understand and interact with the information in a meaningful way.
Challenges of Data Preprocessing
Now, if data preprocessing was a walk in the park, we'd all be sipping piña coladas on a beach somewhere. But alas, it's not quite that simple. Here are some of the key challenges we face:
Different Document Formats, Different Content Cues: Imagine trying to navigate a city with a map written in hieroglyphics – that's essentially what our language models face when dealing with various document formats. An HTML file might use tag names to indicate titles or lists, while a PDF relies on visual cues. It's our job to decipher these cues and translate them into a common language our models can understand.
The Need for Standardization: In an ideal world, our applications wouldn't care whether a document is an HTML file, a PDF, or a handwritten note from your grandma. By standardizing these different formats, we can treat all documents equally and process them in a consistent manner. But standardization is easier said than done when each format has its own unique quirks and nuances.
Diverse Document Structures: Have you ever tried to follow instructions for assembling a piece of IKEA furniture, only to realize halfway through that you're missing a crucial step? Different document types, like journal articles and forms, have vastly different structures, and we need to account for these structural differences during the preprocessing phase.
Extracting Meaningful Metadata: Remember when we talked about metadata being like labels for our documents? Well, not all metadata is created equal. We need to identify and extract the most relevant metadata that will aid us in downstream operations like filtering and hybrid search. It's like trying to find a needle in a haystack.
Despite these challenges, with the right techniques we can overcome these hurdles and ensure our language models have access to the information they need, when they need it.
Conclusion
We've covered a lot of ground in our exploration of LLM data preprocessing, from understanding its importance in RAG applications to tackling the various challenges and intricacies involved.
While data preprocessing might not be the most glamorous aspect of machine learning, it's an essential step that ensures our language models can effectively understand and leverage the wealth of information we feed them.