As a Platform Engineer, I would like to run a script on over 1000 servers and I do not want to spend the whole day running the script manually. There are times when Engineers are given a task that involves running the script on numerous servers; this process can be automated using Ansible.
What is Ansible? Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for application deployment, orchestration, and configuration management. Ansible is designed to simplify complex tasks for instance infrastructure provisioning, configuration management, and software deployment across a large-scale environment. Ansible uses YAML (YAML Ain’t Markup Language) syntax to describe configuration and automation tasks.
You are given a task to run a command to detect theTimezoneon 1000 servers because one of the Quality Engineers detected that some transactions are dated in the future and the engineers suspected that some servers might have incorrect timezones. You are given a file that contains the IP addresses of 1000 servers.
I will be walking you through the process of achieving this task using Ansible. This is an assumption that you already have an understanding of Python, Ansible, and Bash.
Step 1
Establish a passwordless SSH connection with the target host, this will enable Ansible to securely login into the target host without having to receive a prompt to input the password.
Step 2
Add the IP address to the file servers.txt and ensure the IP address is valid and follows the format as it is in the servers.txt
Step 3
Extract the server IP Address using Python; to dynamically generate the inventory file
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import re
import json
import os
# Get the current directory
current_directory = os.getcwd()
# Concatenate the current directory with the file name
server_file = os.path.join(current_directory, 'servers.txt')
def read_servers_file(server_file):
"""Reads the server file and extracts the IP addresses."""
ips = []
with open(server_file, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
if 'ip_address=' in line:
match = re.search(r'ip_address=([\d\.]+)', line)
if match:
ips.append(match.group(1))
return ips
def generate_inventory(ips):
"""Generates the inventory in JSON format."""
inventory = {
'_meta': {
'hostvars': {}
},
'all': {
'hosts': ips
}
}
return inventory
def main():
"""Main function."""
ips = read_servers_file(server_file)
inventory = generate_inventory(ips)
print(json.dumps(inventory))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Step 4
The Ansible Playbook below will run a command date on the target servers and will display the output in a file called report.txt
---
- name: Extract ctlplane IP addresses and run command on servers
hosts: all
gather_facts: yes
become: yes
remote_user: ec2-user #change this to the remote user
tasks:
- name: Run command on servers and save output locally
ansible.builtin.shell: "date"
register: command_output
run_once: yes
- name: Debug command output
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ command_output.stdout }}"
- name: Create your local file on master node
ansible.builtin.file:
path: "report.txt"
state: touch
mode: '0644'
delegate_to: localhost
become: no
- name: Create report.txt file or append to existing file
ansible.builtin.lineinfile:
path: "report.txt"
line: "{{ item }} - {{ command_output.stdout }}"
loop: "{{ ansible_play_batch }}"
delegate_to: localhost
become: no
Step 5
To run the Ansible playbook. Use this command ansible-playbook -i dynamic_inventory.py ansible-playbook.yml
Step 6
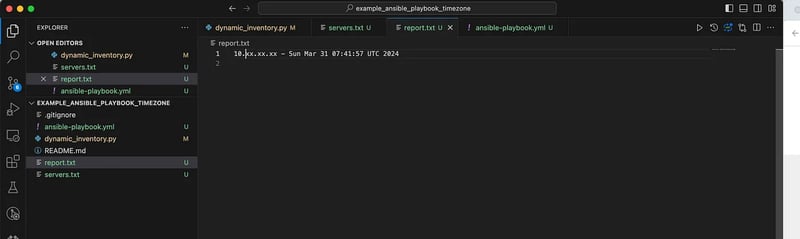
You should have a similar output as the one we have below in the screenshot
In Conclusion, I do hope you find this article useful and interesting. It demonstrates the procedure on how to run an Adhoc script using Ansible by dynamically generating the inventory file. Follow this link below to check the complete code on GitHub https://github.com/ExitoLab/example_ansible_playbook_timezone