The first chapter of this PyQGIS tutorial series told about basic commands and approach of PyQGIS module.
This second chapter tell you about how to manage layers with some usual commands.
You can use your own data or use a sample data of Paris region cities from France government platform.
1. Open script editor of Python Console
In Python console we can launch commands one by one, but we need several commands to manage layers.
To run those at once, we need to open the script editor.
1.1. Open Python console in QGIS
As for the first chapter :
Open QGIS, menu -> Plugins -> Python Console

Or use shortcut Ctrl+Alt+P (Windows) command+option+P (mac)
Python console open usually at the bottom of QGIS frame
1.2. Open Script Editor
Click on the Show Editor button to open script editor as below:
2. Layer related commands
Here are some basic commands to manage layers in a QGIS project.
2.1. Import layer from file
Layer can be load in QGIS with two commands:
# 1- declare a new layer and specify file_path and layer name
layer = QgsVectorLayer(file_path, layer_name, "ogr")
# 2- import declared layer
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(layer)
On script editor, copy the following code, adapt to the file you want to import, and run.
file_path = "your/path/data/target_file.shp"
layer_name = "my fantastic layer"
# declare a new layer and specify file_path and layer name
layer = QgsVectorLayer(file_path, layer_name, "ogr")
# import declared layer
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(layer)
2.2. Import only a part of features from file
We can import a part of features by filtering declared layer.
The following command will filter data where
target_field = 'target_value'
and it should be put before import command.
layer.setSubsetString("target_field='target_value'")
In process, layer name will be added with 'filtered' suffix:
file_path = "your/path/data/target_file.shp"
layer_name = "my fantastic layer filtered"
# declare a new layer and specify file_path and layer name
layer = QgsVectorLayer(file_path, layer_name, "ogr")
# filter layer before import
layer.setSubsetString("target_field='target_value'")
# import declared layer
QgsProject.instance().addMapLayer(layer)
On below pic, data is filtered with only Paris' wards with:
layer.setSubsetString("numdep=75")
2.3. List layers
There are various ways to list layers: we can retrieve layers as object or just layers name.
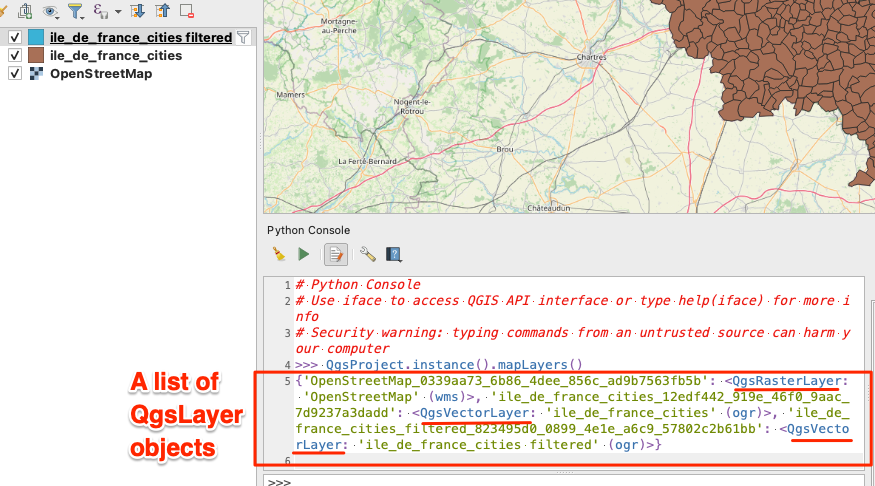
- Running following command directly on python console will show a list of layer, not by layer name, but by object showing layer ID, and their PyQgis type: ```python
QgsProject.instance().mapLayers()
- Adding `.values` on above result will reduce response to class and layer name:
```python
QgsProject.instance().mapLayers().values()
To retrieve only layers' name, use the .name() attribute of each layer object:
for layer in QgsProject.instance().mapLayers().values():
print(layer.name())
2.3. Retrieve a layer by name
A layer can be retrieved by name with the following command:
QgsProject.instance().mapLayersByName("search_layer_name")
This is the main way to retrieve a layer and manipulate it.
This command will not return layer, but a list of layers which fit to target name.
So, to get layer as unique, you can add an iteration like [0], which means the first matching of returned list:
QgsProject.instance().mapLayersByName("search_layer_name")[0]
2.4. Remove layer
removeLayer method of QgsProject.instance() is used.
As written in documentation, target layer ID is required.
layer ID can be retrieved with by adding .id() method of layer class that we retrieved in previous step.
layer = QgsProject.instance().mapLayersByName("search_layer_name")[0]
print(layer.id())
Thus, we can use this id to remove layer.
layer = QgsProject.instance().mapLayersByName("search_layer_name")[0]
QgsProject.instance().removeMapLayer(layer.id())
3. The use of QgsProject class to manage layers
In this second chapter, QgsProject.instance() has been mainly used to add, retrieve and remove layer.
Regarding documentation, many other manipulations can be done, such as remove all layers or manipulate other project matters.
Retrieving layers as objects also makes introduced us to QgsVectorLayer which will be the topic of the next chapter.




























