The saying "users make or break businesses" is also true for your Linux server, and literally, too 😉. As a cloud engineer, understanding how to manage users is non-negotiable.
In this article, I'll distill everything you need to know about users practically so you can grasp how to handle them on your servers.
Let's start with users in the next section.
For this article, I have set up an Ubuntu desktop virtual machine on my system. However, you should be able to follow along with any Linux system you have, either virtual or physical.
Users
Users, as the name implies, are users of your Linux server, including you (yes, you are but a user that can be modified and even removed, so thread carefully 🫵🏾).
Users represent anyone with access to your server (no matter how little). These include but are not limited to employees, accountants, analysts, HR, etc. However, users are not always people; you can also create system users with access to the server to start, process, and stop the automated tasks you have created.
Understanding the root User
At any point in time, you have at least two users on your Ubuntu server: the user you created (system administrator) when setting the server up and root (this may be different for other platforms).
The root account is created automatically, and it is the most powerful account on your server (yes, it's not you, well technically 😉) because it can be used to do anything on the server; yes, and that includes deleting the server itself. No questions asked (yes, not even a confirmation from you) and that is why you were asked to create a user while setting up the server because you should ONLY use the root account when you have to.
Understanding the sudo Command
Now that you understand the power of the root account, as a regular user, you might need its power sometimes to perform some system-altering tasks like installing or deleting packages, and that's where the sudo command comes in (insert the Money Heist meme).
The sudo command gives you the power of the root account as long as you can provide the requested password. You will have to use sudo for all system-altering commands or any command that you don't have access to usually. sudo is used by prefixing any command with it like so:
sudo apt install ufw
The command above will prompt you to type in the system password before installing the specified package.
Now that you understand users, root, and how to invoke the higher powers using sudo, let's start creating users in the next section.
Creating Users
You can use two commands to create a user in Linux, and we'll explore both in this section.
Adding Users with the useradd Command
The useradd command is arguably the most straightforward command for creating users. Here's how to create a user and their home directory at the same time:
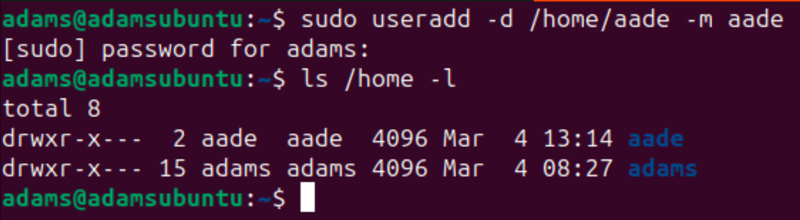
sudo useradd -d /home/aade -m aade
The command above used sudo to add a user and its directory because it is a system-altering command. The -d flag is used to create the home directory /home/aade while the -m flag is used to specify the preferred username.
You can now run the following command to see all the users with a home directory:
ls /home -l
You should see something like this:
Now that you've added a user so seamlessly, you might ask: "won't they need a password?" since you were not asked to specify that while creating the user. Well, I've got you! You can add a password for the user using the following command:
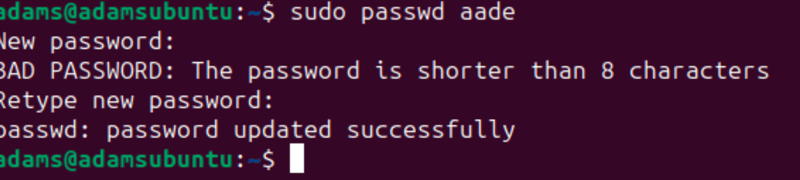
sudo passwd aade
After running the above command, you will be prompted to type and retype in a new password like so:
Note: Not seeing a visual representation of the password for security is standard. However, make sure you add a strong password for your users 😉.
Adding Users with the adduser Command
The previous section is sufficient enough to know how to create users. However, if you want to add a full name and password while creating a user in one go, you can use the useradd command for that like so:
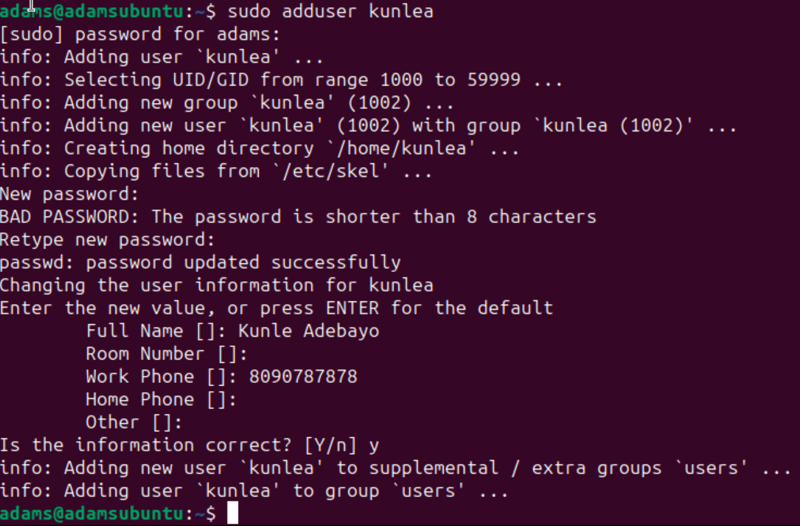
sudo adduser kunlea
The command above should prompt you for more information about the user like so:
Note: Despite being straightforward and convenient,
adduseris not available on some Linux distributions.
You have now added two users with their home directories, and you can check it by rerunning the following command:
ls /home -l
Next, let's explore how to remove users in the following section.
Removing Users
Removing users from your server is very straightforward. However, you need to consider whether you want to remove the user files, too.
For example, if user kunlea is leaving the company, you might want to remove them from the server while retaining their files (documents they worked on) for later use even if they don't have access to them anymore. However, if the company has a backup policy/storage, you can copy kunlea's files to the backup and delete the user and its files simultaneously.
You can move kunlea's files to the backup using the mv command like so:
sudo mv /home/kunlea ~/employee_files_backup
The command above will move the home directory files to the employee_files_backup folder. You can now delete kunlea alongside their home directory like so:
sudo userdel -r kunlea
Now that you understand how to create and remove users let's explore how to access user information in the following section.
Accessing User Data
You can access user data as the server administrator using the /etc/passwd file. Run the following command to view the content of the first file:
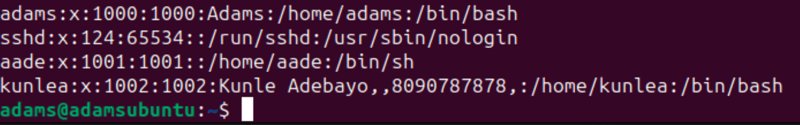
cat /etc/passwd
The command above should return a lot of content, but my last four lines would look something like this:
Each line in the result above has multiple columns separated by a colon :. Let's explore what each column (of the user we created in the previous section) means.
- The first column is the username of the user (remember: this can be a person or a system user)
- The second column is the password represented by an
xfor security reasons. - The third column is the user ID (UID).
- The fourth column is the group ID (GID).
- The fifth column is the General Electric Comprehensive Operating Supervisor (GECOS), which is empty for all users except
kunleabecause we filled in that information while using theaddusercommand. - The sixth column is the home directory of the user
- The seventh column is the default login shell for the user.
/bin/bashforkunleabecause we usedadduserand/bin/shforaadebecause we useduseraddto create it.
There are other users you did not create called Default Users, which you'll probably never have to interact with (keep an open mind, tho 😉).
Now that you know enough to start managing users, let's explore how to switch users in the next section.
Switching Users
As a system administrator, switching to a newly created user is recommended to ensure they can log in and have permission to do things you allow and not let things you don't give them access to.
Let's start by switching to the root account.
Switching to root Account
I explained the root account in a previous section but didn't show you how to switch to it. You can switch to the root account with the following command:
sudo su -
The command above will allow you to access the server as root, but remember, only do this if you have to.
Switching to Other Users
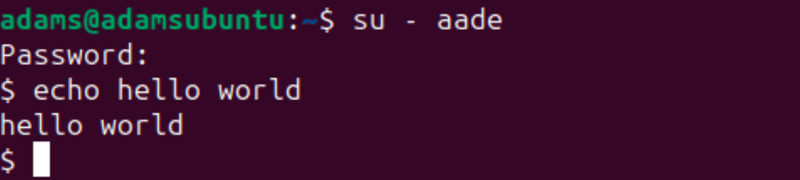
To ensure your users have access to the server before you give them their details, you can access the account like so:
su - aade
The command above will ask you for the user password (if it has one) and log you in as the user like so:
You can switch back to the previous account with the following command:
exit
Switching Users Without Password
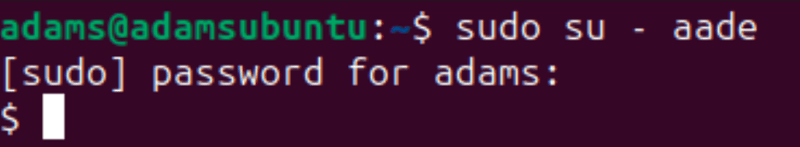
You can also switch users even if you don't have their password by using sudo like so:
sudo su - aade
The command above will request the sudo password instead of the user's password to log you in like this:
Now that you understand how to create, delete, and switch users, let's explore how to create default configuration files for all users.
Creating Default Configuration Files for Users
Using the analogy that each user in your server is an employee, you might want to give all new employees a set of employee handbooks, contribution guides, and base rules and regulation files.
To do that, you can create and add the files into the /etc/skel directory, which will then distribute the files into the home directory of every new user you create with a home directory.
First, create the files in your directory:
touch rules_reg.txt employee_handbook.txt contrib_guide.txt
Next, copy the files into the /etc/skel directory with:
sudo cp rules_reg.txt employee_handbook.txt contrib_guide.txt /etc/skel
The command will prompt you for the sudo password before copying the files into the directory.
Next, create a new user with a home directory like so:
sudo useradd -d /home/kolapo -m kolapo
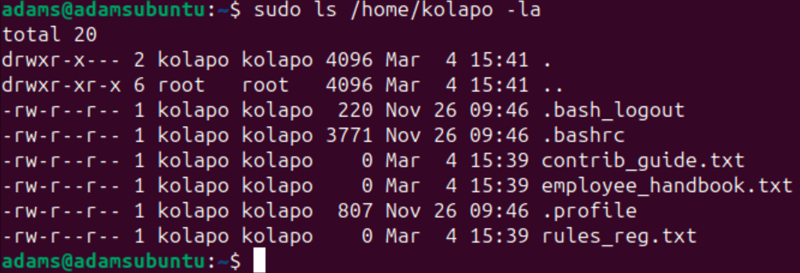
Lastly, list the content of the new user's home directory like so:
sudo ls /home/kolapo -la
The command above should list the files you copied to the /etc/skel alongside the default files like so:
Conclusion
I hope this article achieved its aim of getting you started managing users in Ubuntu on the right foot. You learned what users are in Linux, how to create, delete, switch users, and much more.
Finally, remember to follow me here on Dev, LinkedIn, and Twitter. Thank you so much for reading, and I'll see you in the next one!