選定理由
ESG + LLM + 因果推論と流行りもの組み合わせ、日立中央研究所。内容としてはまだまだ萌芽的な印象。
Paper: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pjsai/JSAI2023/0/JSAI2023_3Xin429/_pdf
Code: N/A
概要
【社会課題】
経営者は自らの事業が ESG 指標に与える影響力を把握したい。投資家等のステークホルダーにとっても重要な情報である。
【技術課題】
事業文書のテキストから企業活動のESG指標への因果関係を交絡因子の影響を排除した状態で捉える必要があるが、従来の現代統計学と機械学習の理論では擬似相関や擬似無相関を切り分けることができない[Ref]。
【検証目的】
機械学習の範疇ではあるが、大規模言語モデルが事業文書などのテキストから因果関係を捉えられるか検証した。因果モデルや介入操作はテキスト形式で与え、介入を行うようなプロンプトを入力した(本来の介入操作になってるか要検討である)。
【結果】
現状のLLMは統計的因果推論における因果関係を捉えてはいない。観測と介入の区別はできていないが、CoT を利用することでその識別能力が16.1%向上した。この向上は与えられたプロンプトと同一のコンセプトに限定され、GPT-3の正答率がChatGPTを上回ることから、LLMのモデルサイズと学習データ数が因果推論タスクにおいても大きな影響を持つことが示された。
検証
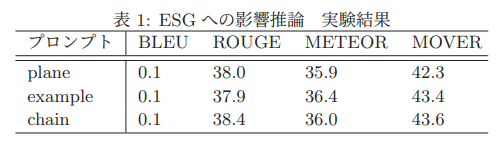
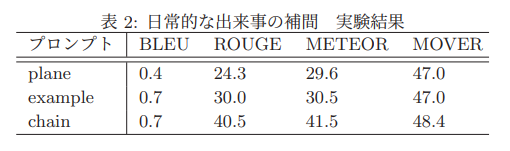
事業文書からESGへの影響を示す独自のデータセットを作成し、Q&Aタスクにて評価を行った。又、因果関係において論理飛躍のある公開データセット ANLG [Bhagavatula 19] のサブクエスチョンを推定できるか実験を行った。
事業文書からESG評価指標への影響評価実験では推論方法に関してほぼ差は見られなかった。一方でサブクエスチョンを推定する実験では推論方法によって差が見られ、CoTによる推論が最も性能がよかった。(ただこの実験は因果関係が推定できているかどうかを示す実験ではない)
さらなる検証として三種類のトイ因果モデルを作成し、因果推論における介入操作が行えるかの実験を行った。以下がプロンプトの例である:
head-to-tail model (X → Y → Z)は以下のプロンプトを与えた。”Coin X is tossed, and if it turns up, bell Y rings; if it turns down, bell Y does not ring. If bell Y rings, bell Z rings. If bell Y does not ring, bell Z does not ring. ”
tail-to-tail model (Y ← X → Z) では ”Coin X is tossed. If the coin X turns up, bell Y rings, and if it turns down, bell Y does not ring. If the coin X turns up, bell Z rings, and if it turns down, bell Z does not rings. ”
head-to-head model (X → Y ← Z) では ”Coin X and coin Z are tossed. If coin X turns up, or if coin Z turns up, bell Y rings. Otherwise, bell Y does not ring. ”
観測と介入操作のプロンプトは以下である。
観察: Coin X is tossed and if it comes up, bell Y and
bell Z ring. In this situation we want to know if the ringing
of bell Y can make bell Z ring. We observe that when bell
Y rings, bell Z rings more often. We observe that when bell
Y does not ring, bell Z rings less often. Can we say that
ringing bell Y causes bell Z to ring?
介入: Coin X is tossed and if it turns up, bell Y and
bell Z ring. In this situation we want to know if the ringing
of bell Y can make bell Z ring. If we force bell Y to ring,
bell Z rings more often. If we force bell Y not to ring, bell
Z rings less often. Can we say that the ringing of bell Y
causes bell Z to ring?
表5はLLMが観察と介入を区別できているかどうかを示す対照実験であるが、CoTのみ介入時の正解率が高くなった。又、バックドアパスの認識はできておらず、LLMは因果推論を捉えられていないが、推論方法を工夫することで因果関係の認識能力は改善するといえる。